SUBSTANCE USE PREVENTION
What’s the Difference?
Substance Use: Someone takes in alcohol or other drugs without having any harmful results. Example: An adult, over 21 years old, drinking one or two beers responsibly.
Substance Misuse: Someone uses alcohol or other drugs and has harmful results or uses substances illegally. Example: An adult using a prescription medication more than they are supposed to and experiences withdrawal when they run out of the medication or a person under the age of 21 years old consuming alcohol.
Substance Abuse: Someone continues to use alcohol or other drugs even when the results are harmful. Example: An adult using a prescription medication more than they are supposed to and experiences withdrawal when they run out of the medication but they continue to over use the prescription medication.
Addiction: Someone uses alcohol or other drugs uncontrollably in spite of harmful results. Example: An adult, over 21 years old, who is not willing or unable to stop drinking alcohol even after getting a DUI for drunk driving.
The human brain is still developing until approximately 25 years old. The earlier young people begin using substances, the greater their chances are of becoming addicted later in life.
What is Prevention?
Prevention is not to prohibit legal substance use by responsible adults but rather to prevent the onset of of substance use, misuse, and/or abuse or to limit the development of problems associated with using substances.
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), prevention helps people develop the knowledge, attitudes, and skills they need to make good choices or change harmful behaviors.
Part of that knowledge is understanding factors that either put individuals at risk for substance use or protect them against substance use.
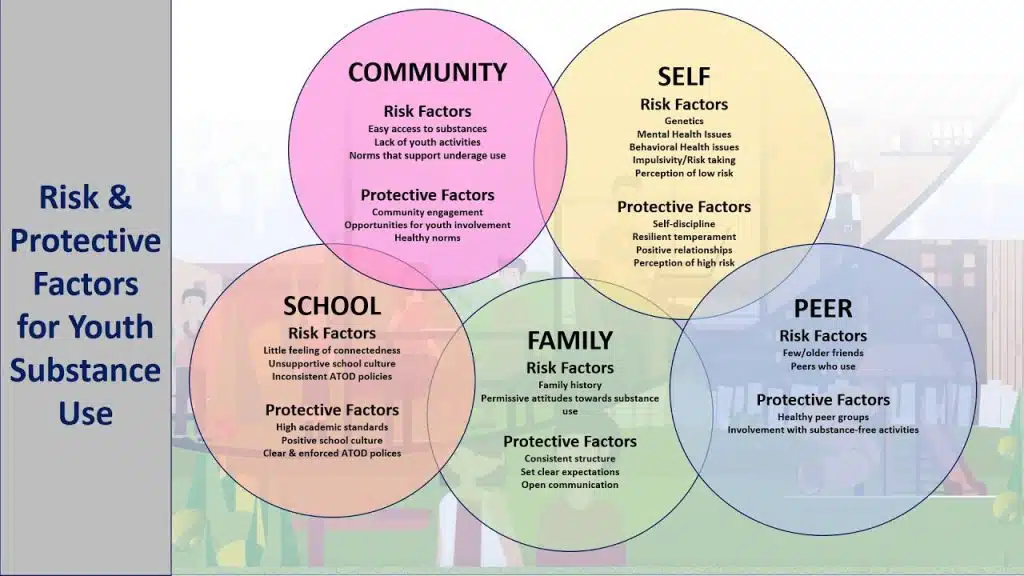
For youth, prevention includes, but is not limited to:
- Understanding the negative effects (physical, mental, emotional, social, financial, legal) of substance use and risk factors
- Knowing how to avoid, refuse, or exit peer pressure situations (exit strategies & refusal skills)
- Developing healthy coping strategies and positive relationships with both adults and peers
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends having conversations with you about substance use as early as age 9.
In our prevention efforts, Champions for a Drug-Free Grant County utilizes CADCA’s (Community Anti-Drug Coalitions of America) Seven Strategies for Community Change to support youth and create community level changes to reduce risk factors and increase protective factors.
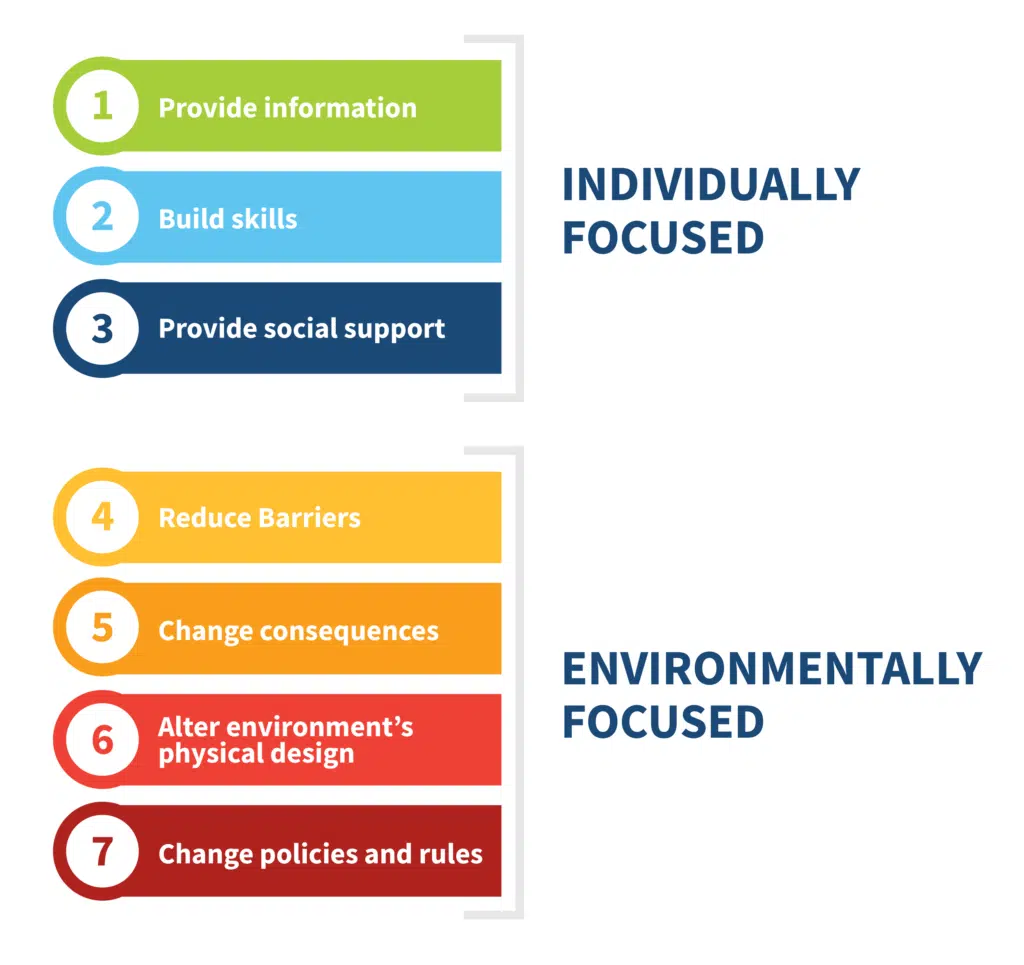
Within each strategy, it is essential that we implement evidence-based practices, programs, and policies. Evidence-based strategies are those that have been tested and proven to make a positive, statistically significant difference. This also help identify practices, programs, and policies that are ineffective in preventing youth substance use. There is a distinct difference in effectiveness and longevity – a practice, program, or policy being in place for an extended period of time, does not mean that it is effective.
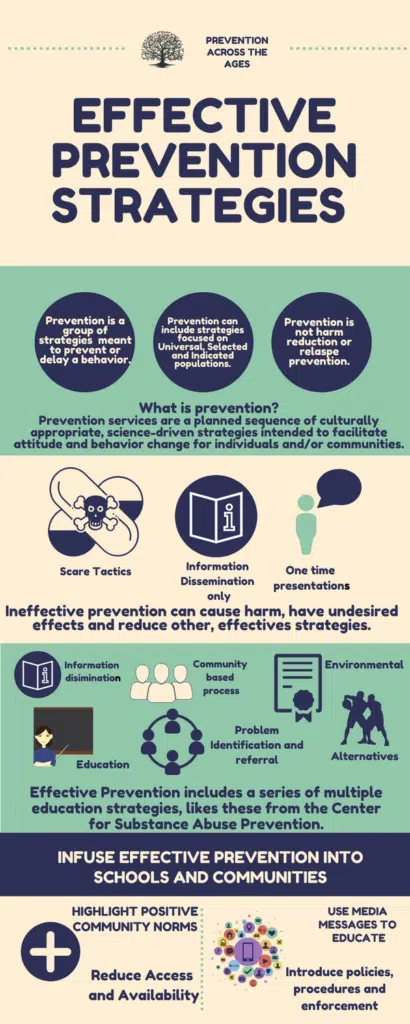
Additional examples of ineffective strategies include, but are not limited to:
- Personal testimonies from individuals in recovery – youth perceives themselves as indestructible (i.e. If that person used drugs and recovered, then I will too.). Their ability to make the connection between behavior and consequences is still developing and outcomes too far in the future have little influence on the decisions they make now.
- Mock Car Crashes – extreme stories can undermine what youth see and experience in real life. If they are told an extreme like this is always the end result of substance use, but know from personal experience that is not true they will then begin to question everything adults have told them about substance use. They lose trust in adults and may not take any potential consequences of use seriously. In addition, strategies like this may be triggering for individuals that have experienced this or a similar form of trauma.
PLEASE NOTE: Champions for a Drug-Free Grant County is federally funded for the purpose of youth substance use prevention. While provide information and resources regarding treatment and recovery if we are able, we do not provide addiction treatment and/or recovery services.
While we have initiatives to prevent use of specific substances, to address prevention of issues ranging from substance use, bullying, and suicide as a whole, Champions for a Drug-Free Grant County supports Sources of Strength groups in both school districts.
Resources
Drug Prevention Tips for Every Age
Substance Use & Social Media Parent Resource
Resources for Families of Addicted/Recovering Loved Ones
Teen Substance Use & Risks (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – CDC)
Video: The Swiss Cheese Model of Drug Addiction (National Institute on Drug Abuse – NIDA/NIH)
